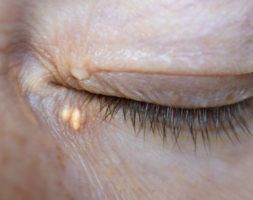
Acne is a very common dermatosis ( a skin disease ) which generally starts at puberty, affecting the adolescence of 85% of people, regardless of ethnic background.
The main drawback is its unsightly appearance. Acne can have a psycho-social impact which we should not under-estimate.
Acne is a disease of the pilosebaceous follicles, developing in a variable fashion, for which the physiopathology identifies three stages: sebaceous hypersecretion; formation of retentional lesions : comedogenesis ( the formation of blackheads ) and the formation of inflamed lesions: papules, pustules and nodules.
ANALYSIS
THERE ARE RETENTIONAL LESIONS AND INFLAMMATORY LESIONS
Retentional lesions
Seborrhea is often the first manifestation of acne. This excess of sebum is responsible for the shiny appearance of the skin, dilated pores and the formation of retentional lesions: whitehead and blackhead.
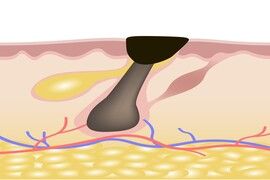
Blackhead
The blackhead or open comedo is constituted by a mixture of sebum and cells of the wall of the hair canal.
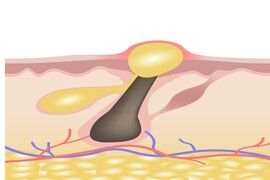
whitehead
The microcyst or whitehead is clinically presented as an indurated and localized bulge of the skin centered by a white area.
It corresponds to a sebaceous pilose follicle whose orifice of the hair canal is covered with cells of the epidermis which seal it.
Inflammatory lesions
The inflammatory phase begins as soon as there is enough bacteria in the sebaceous gland to cause a defense response of the body and inflammation of the follicle.
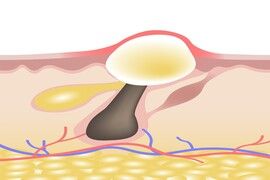
Pustules
The papules are red elevations, one to four millimeters in diameter, surrounded by an inflammatory halo.
The pustules surmount the papules, they are inflammatory containing pus. They can evacuate or form nodules by breaking in the deep layers of the skin.
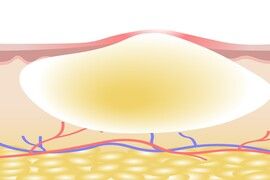
Acne nodules
Nodules correspond to a deeper attack of the skin and have a long evolution. They are the ones who can leave scars and sometimes have to be evacuated surgically.
THERE ARE FIVE STAGE OF GRAVITY
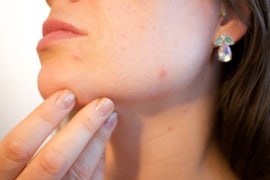
Very light (Grade1)
Virtually no injury.
Rare comedones.
Open or closed.
Scattered and rare papules.
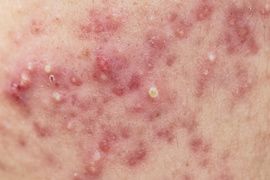
Severe (Grade5)
Very inflammatory acne covering the face with nodules.

Light (Grade2)
Easily identifiable.
Less than half of the face is affected.
Some comedones.
Open or closed, and some papulo-pustules.
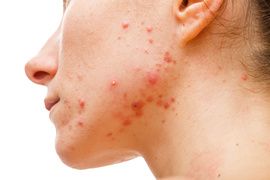
Mild (Grade3)
More than half of the face is affected. Many papulo-pustules, many open and closed comedones.
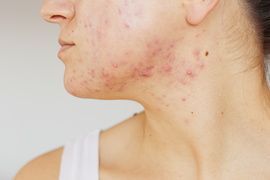
Moderate (Grade4)
The whole face is affected, covered with many papulopustules, open and closed comedones and rare nodules.
THERE ARE SEVERAL TYPES OF SCARS
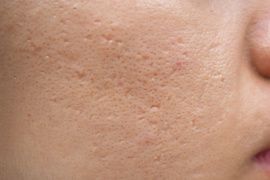
Atrophic scars
Atrophic acne scars are the most common, appearing as a form of depression on the skin’s surface, due to a loss of tissue above the base of the scar. They do not heal spontaneously.
Three types atrophic scars exist ( according to their contour, shape, the base and depth ): ice-pick or V-shaped scars; boxcar or U-shaped scars and rolling or M-shaped scars.
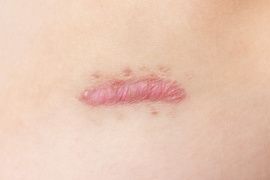
Hypertrophic scars
Basic hypertrophic scars will regress more or less spontaneously in 12-18 months.
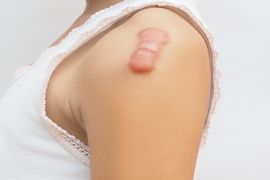
Keloid scars
Keloid scars do not regress spontaneously.

Erythematous macules
Pigmented or erythematous ( inflamed, rash like ) macules follow the scarring process of inflammatory acne surface wounds. Erythematous macules often disappear without trace in a few weeks, while pigmented macules regress very slowly.
POSSIBLE TREATMENTS
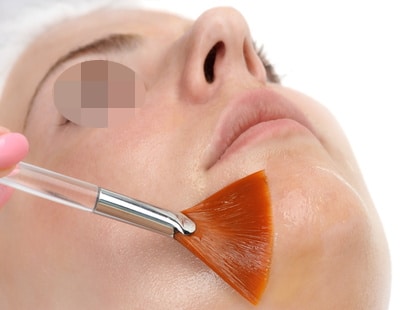
Peel
Peels, especially those based on salicylic and glycolic acid, reduce inflammation of acne lesions and seborrhea of the face and stimulate skin regeneration.
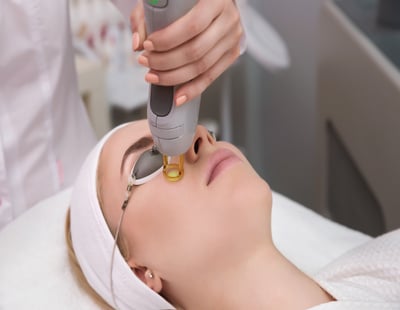
Laser
Lasers, can help by reducing the total bacteria (Proprionibacterium acnes) and by reducing the size of sebaceous glands, and thus the production of sebum.
Lasers and lamps which act on Proprionibacterium acnes are:
– Blue light, thanks to pulse lamps (which have a spectrum of excitation of about 400nm).
– KTP laser (532 nm).
– All Pulsed Dye Lasers (585 and 595 nm)Lasers which act on the sebaceous glands.
– Infrared lasers:
1) Lasers at 1320 nm.
2) Lasers at 1450 nm.
The diode 1450 nm laser (the ‘Smoothbeam’) is strongly absorbed by water, resulting in a maximum heat effect in the papillary dermis, at a depth of about 200-400 microns. The sebaceous glands are at this depth. The created heat leads to the fibrosis of the sebaceous gland, and greater collagen production. The aim is to gradually heat the upper dermis (surface layer) without damaging the epidermis, hence without burning it.
A slight red rash (erythema) can last from a few hours to a few days after the treatment, but it is easy to cover with make-up.
3 or 4 sessions will be needed, at an interval of one month.
3) 1540 nm. The Er-Glass 1540 nm ARAMIS laser acts on the sebaceous glands and the follicular infundibulum. Thanks to the length of its waves, absorbed by the targets and water, and barely captured by melanin, the treatment is suitable for dark and tanned skins. 3 or 4 sessions will be needed, at an interval of one month.
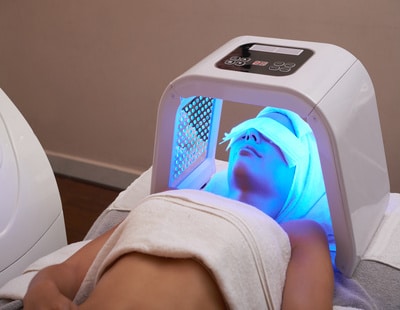
LED
Light exposure has long been used to reduce acne. In cases of mild to moderate acne, LED phototherapy uses blue light to attack the Proprionibacterium acnesbacteria, and red light for its anti-inflammatory action.
.
Testimonials-reviews
A. BRIXTON
B. BUSH
L. MORRIS
R. MILTON